Home » Medical Conditions » PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal condition that affects many women of reproductive age. It usually begins during adolescence and often causes fluctuating symptoms over time.
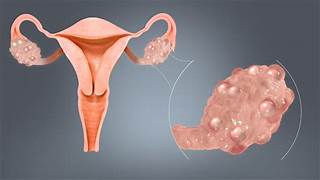
What are the Symptoms of PCOS?
Causes:
Diagnosis:
Treatment:
Outlook: